Input
1
4 8 2
1 2 4
1 3 2
1 4 7
2 1 1
2 3 5
3 1 2
3 4 4
4 2 3
Output
#1 10
임의의 정점 [x]과 나머지 정점들을 [i]라고 했을 때,
[i] → [x] → [i]까지의 최단 거리 비용이 가장 큰 비용을 구하는 문제입니다.
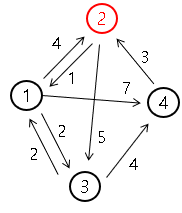
구현
플로이드 와셜 알고리즘을 이용해서 모든 정점들의 최단 거리 비용을 구할 수 있지만,
[1 ≤ N ≤ 50,000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 500,000]이기에 TLE 발생
그렇기에 다익스트라(Dijkstra) 이용
다익스트라 (Dijkstra)
개념 다익스트라 알고리즘은 Single Source shortest path problem으로 하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점까지 최단 경로를 구할 때 주로 사용됩니다. 이때, 간선의 가중치는 only 양수가 전제조건입니다. (
zoosso.tistory.com
※ 동일한 내용의 문제로 플로이드 와샬 (Floyd Warshall) 알고리즘 적용 가능
플로이드 와샬 (Floyd Warshall)
개념 아래와 같은 가중 그래프에서 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘. ex) 정점 ③ → ⑤로 가는 최단 경로는 다음과 같습니다. 경로Path: ③ → ② → ④ → ① → ⑤ 비용Cost: +4 +1 +2 -4 = 3..
zoosso.tistory.com
※ 참고문제: [BOJ] 1238 파티
[BOJ] 백준 1238 파티
출처: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1238 Input 4 8 2 1 2 4 1 3 2 1 4 7 2 1 1 2 3 5 3 1 2 3 4 4 4 2 3 Output 10 다른 정점들로부터 특정 정점까지의 최단 거리 비용을 구해야 하므로 플로이드 와샬 (F..
zoosso.tistory.com
다익스트라는 특정 정점 [x]에 다른 정점들까지의 최단 거리 비용을 구하는 알고리즘입니다.
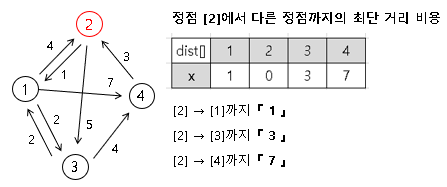
그렇기에 [x] → [i]에 대해서는 주어진 그래프를 바로 이용하면 되지만, ← O(E log E)
[i] → [x]에 대해서는 결국 정점 [x]를 제외한 각각의 정점 [i]에 다익스트라 알고리즘을 적용해서
정점 [x]로 가는 최단 거리 비용을 구해야 합니다. ← O(V * E log E), 결과적으로 TLE 발생
path: [i] → [x] → [i]에 대한 최단 거리 비용이므로, [i] → [x]에 대한 최단 거리 비용을 구할 때는
그래프의 간선의 방향을 반대로하여 다익스트라 알고리즘을 적용합니다.

Graph 1, 2에서 정점 [x] → [i]에 대한 최단 거리 비용을 구합니다.
(Graph 2에서 구한 결과가 기존 그래프에서 [i] → [x]에 대한 최단 거리 비용과 동일)
▶ [4] → [2] → [4] = 3 + 7 = 10
※ 그래프 구현하는 방법
그래프 정의 및 구현 방식 (인접 행렬 & 인접 리스트)
그래프 정의 및 구현 방식 (인접 행렬 & 인접 리스트)
그래프는 G(V, E)는 어떤 자료나 개념을 표현하는 정점(vertex)들의 집합 V와 정점을 연결하는 간선(edge)들의 집합 E로 구성된 자료 구조로 객체들의 상호 관계를 표현하기 위해 고안된 자료 구조입
zoosso.tistory.com
그래프 표현 (인접 리스트 / 인접 행렬)
정점 u - v 간 간선 여부 확인 - 인접 리스트는 adList[u]의 처음부터 읽어나가면서 각 원소를 일일이 확인 - 인접 행렬은은 정점 u, v가 주어졌을 때, 단 한 번의 배열의 접근으로 연결 여부 확인 공간
zoosso.tistory.com
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Solution {
static final int INF = 1000000000;
static int N, M, X;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = null;
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int tc=1; tc<=T; tc++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 개수
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 개수
X = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
List<List<Node>> adList = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Node>> adList2 = new ArrayList<>();
// 인덱스를 1부터 하기 위해 임의로 한 개를 넣어둠
adList.add(new<Node> ArrayList());
adList2.add(new<Node> ArrayList());
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
adList.add(new<Node> ArrayList());
adList2.add(new<Node> ArrayList());
}
while(M-- > 0) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int u = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
adList.get(u).add(new Node(v, cost));
adList2.get(v).add(new Node(u, cost));
}
// dist[] INF로 초기화
int[] dist = new int[N+1]; int[] dist2 = new int[N+1];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF); Arrays.fill(dist2, INF);
// 다익스트라 알고리즘
dijkstra(X, adList, dist);
dijkstra(X, adList2, dist2);
int answer = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.print("#" + tc + " ");
for (int i=1; i <= N; i++) {
// 연결된 정점이 아닌 경우
if(dist[i] >= INF || dist2[i] >= INF) continue;
answer = Math.max(answer, dist[i] + dist2[i]);
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
private static void dijkstra(int start, List<List<Node>> adList, int[] dist) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[N+1];
dist[start] = 0;
pq.add(new Node(start, 0));
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node current = pq.poll();
// 재방문 여부 확인
if(visited[current.ID]) continue;
visited[current.ID] = true;
// 연결된 정점들을 확인
for(Node next : adList.get(current.ID)) {
// 효율적인 처리를 위해 최소 거리 비용이 갱신되는 경우만 queue에 넣어줍니다.
if(dist[next.ID] > dist[current.ID] + next.distance) {
// 최소 거리 비용 갱신
dist[next.ID] = dist[current.ID] + next.distance;
pq.add(new Node(next.ID, dist[next.ID]));
}
}
}
}
}
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int ID;
int distance;
public Node(int ID, int distance) {
this.ID = ID;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node target) {
// 작은 거리 비용이 먼저 오도록
return this.distance - target.distance;
}
}
'PS 문제 풀이 > SWEA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SWEA] 4006 고속도로 건설 2 (0) | 2021.02.27 |
|---|---|
| [SWEA] 3947 가장 짧은 길 전부 청소하기 (2) | 2021.02.25 |
| [SWEA] 4066 All Pair Shortest Path (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| [SWEA] 3260 두 수의 덧셈 (0) | 2021.02.24 |
| [SWEA] 9780 외계인 침공 (0) | 2021.02.24 |





댓글