반응형
피보나치 수열(Fibonacci Numbers)이란?
1 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 5 → 8 → 13 → 21 → 34 → 55 → 89 → 144 → 233
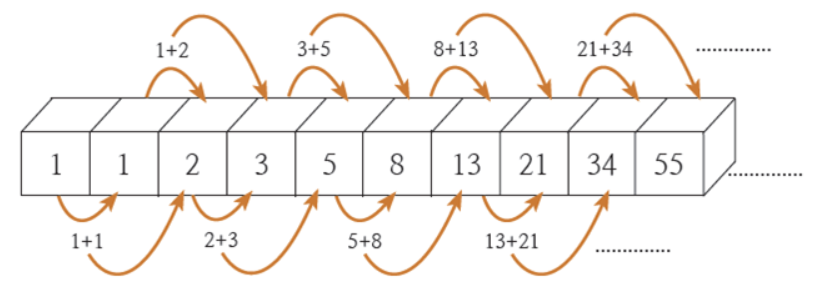
점화식으로 표현하면 다음과 같다.

이를 구현하는 방법은 크게 다음과 같다.
- 재귀 방식 (Recursion)
- 동적 계획 (Dynamic)
재귀 방식(Recursion)
Top-down 방식으로 f(0), f(1)과 같이 작은 부분의 값들이 여러번 호출된다.

public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 40;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println( fibonacci(n) );
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println( "실행 시간 : " + ( end - start ) / 1000.0 );
}
private static int fibonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0) {
return 0;
}else if(n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return fibonacci(n-2) + fibonacci(n-1);
}
}
Top-down 방식은 가독성은 좋지만 중복된 계산을 많이하여
기억 공간을 많이 요구하는 문제(Overhead)가 있다.
동적 계획 (Dynamic)
f(1)~f(n)까지 올라가는 형태로, Bottom-up 방식 사용.
부분 문제부터 전체문제를 해결하는 방식이다.
재귀(Recursion) 방식에서는 f(n-1), f(n-2) 피보나치 값을 계속해서 구하는 문제가 있었다.
그렇기에 동적 계획법에서는 부분 결과값을 기억해서 성능을 높인다.
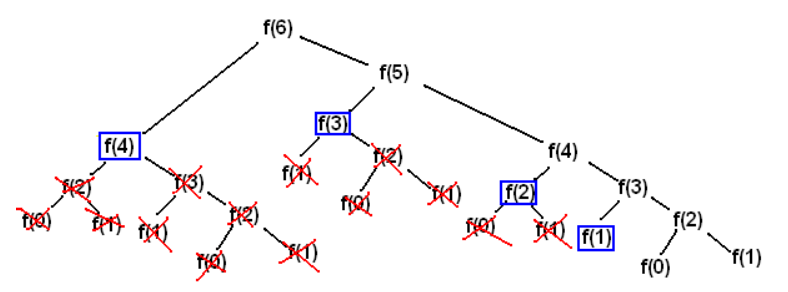
※ [X] 표시를 한 부분은 중복해서 계산되지 않고 [□]만 계산되어 저장된다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 41;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println( fibonacci(n) );
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println( "실행 시간 : " + ( end - start ) / 1000.0 );
}
private static int fibonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0) {
return 0;
}else if(n == 1) {
return 1;
}else {
int[] arr = new int[n];
arr[0] = 0;
arr[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i-2] + arr[i-1];
}
return arr[n-1];
}
}
}
[BOJ] 백준 1003 피보나치 함수
출처: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1003 Input Output C++
zoosso.tistory.com

반응형
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 소수 (Prime Number) 찾기 - 3 (0) | 2021.02.21 |
|---|---|
| 소수 (Prime Number) 찾기 - 2 (0) | 2021.02.21 |
| 소수(Prime Number) 찾기 - 1 (0) | 2021.02.20 |
| 연속된 부분 합(연속합) - 1 (완전 탐색) (0) | 2021.02.20 |
| 세그먼트 트리(Segment Tree) (0) | 2021.02.20 |





댓글