반응형
출처: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2261
Input
4
0 0
10 10
0 10
10 0
Output
100
Brute Force로 모든 점의 거리를 구한 후, 최소 거리를 구하면 → O(N2)으로 TLE 발생
분할 정복 기법을 사용해 → O(N (logN)2)
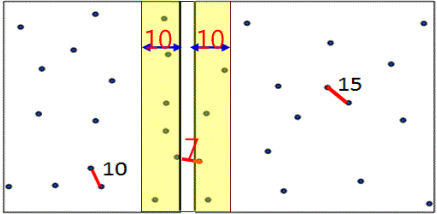
① 모든 점을 x 좌표 기준 정렬 후,
② 중간 지점을 기준으로 두 개로 분할해서 x 구간거리가
일정 수준까지 작아지도록 재귀적으로 분할.

③ merge될 때, 좌측, 우측 부분에서 각각 가장 가까운 두 점 사이의 거리를 구합니다.
좌측, 우측에서 구한 거리 중 더 작은 값을 구합니다.
해당 값이 중간 기준위치를 지나는 왼쪽 점과 오른쪽 점 사이의 거리를 비교합니다.

ex) min(d1, d2) = d를 구한 후, 중간 부분에서 d > d3 를 만족하는 거리(d3)를 구하면 됩니다.
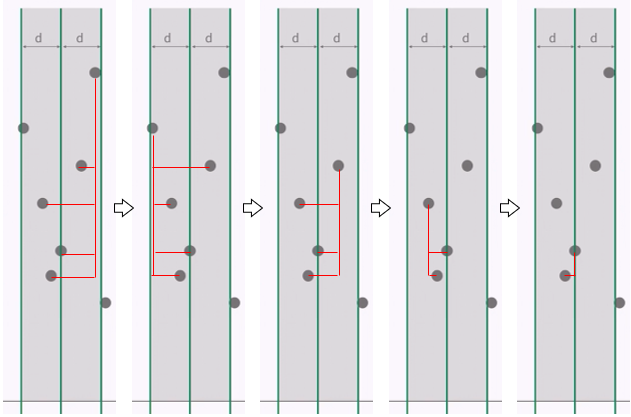
분할 과정을 통해 비교대상을 줄이기는 했지만,
최소 거리를 갱신하기 위해서는 어느정도 완전탐색으로 거리를 비교해야 합니다.

ex) 두 점 사이의 거리 = d = 5일 때, 코드상에서는 제곱처리하여 d * d하여 비교합니다.
④ 중간 부분에서도 마찬가지로 x 좌표상 거리가 『d』 이하인 점들끼리만 실제 거리를 비교합니다.

⑤ x 좌표간 거리가 『d』 이하인 점들을 선별한 뒤로는 y 좌표 기준 정렬
y 좌표간 거리가 『d』 이하인 점들만 선별해서 두 점사이의 거리를 구합니다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = null;
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
List<Point> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr.add(new Point(x, y));
}
// x 좌표 기준 정렬
Collections.sort(arr, new xComparator());
// 정답 출력
System.out.println(closest(arr, 0, N - 1));
}
static int closest(List<Point> arr, int left, int right) {
int sectionSize = right - left + 1;
// 분할된 x좌표상 크기가 3이하이면
if (sectionSize <= 3) {
// 가장 가까운 점의 거리를 구합니다.
return bruteForce(arr, left, right);
}
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
int leftSectionDistance = closest(arr, left, mid);
int rightSectionDistance = closest(arr, mid + 1, right);
// Left Side와 Right Side에서 구한 최소 거리 중 더 작은 값을 전체 구간 중 최소 거리로 임시 설정
int answer = Math.min(leftSectionDistance, rightSectionDistance);
List<Point> middleSection = new ArrayList<>(); // 왼쪽과 오른쪽 사이의 점들을 저장할 List
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
// 중앙을 기준으로 거리를 비교 (제곱하기 때문에 음수는 무의미)
int xDist = arr.get(i).x - arr.get(mid).x;
// x 좌표간 거리가 현재 최소 거리 d 보다 작은 경우만 고려
if (xDist * xDist < answer) {
middleSection.add(arr.get(i));
}
}
// y 좌표 기준으로 정렬 (이제 x좌표 기준은 무의미)
Collections.sort(middleSection, new yComparator());
int candidateSize = middleSection.size();
for (int i = 0; i < candidateSize - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < candidateSize; j++) {
int yDist = middleSection.get(j).y - middleSection.get(i).y;
if (yDist * yDist < answer) {
int dist = findDistance(middleSection.get(i), middleSection.get(j));
if (dist < answer) {
answer = dist;
}
}
// y좌표 기준 오름차순 정렬했기 때문에 기준점과 가장 가까운 좌표가 answer보다 멀면
// 다음 좌표들 비교는 무의미 하므로 break한 후, 다른 좌표를 기준으로 해서 반복
else {
break;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// 완전 탐색으로 가장 가까운 거리 찾기
static int bruteForce(List<Point> arr, int left, int right) {
int answer = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= right; j++) {
int temp = findDistance(arr.get(i), arr.get(j));
if (answer > temp) {
answer = temp;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
// Euclidean Distance의 제곱
static int findDistance(Point p1, Point p2) {
return (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y);
}
}
class xComparator implements Comparator<Point> {
// x 좌표 기준 정렬
@Override
public int compare(Point p1, Point p2) {
return p1.x - p2.x;
}
}
class yComparator implements Comparator<Point> {
// y 좌표 기준 정렬
@Override
public int compare(Point p1, Point p2) {
return p1.y - p2.y;
}
}
class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
반응형
'PS 문제 풀이 > Baekjoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ] 백준 1100 하얀칸 (0) | 2021.02.28 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ] 백준 10950 A + B - 3 (0) | 2021.02.28 |
| [BOJ] 백준 11758 CCW (0) | 2021.02.28 |
| [BOJ] 백준 4354 문자열 제곱 (0) | 2021.02.28 |
| [BOJ] 백준 3055 탈출 (0) | 2021.02.27 |





댓글